CFD works best as one of many tools available for analysis of fluid mechanics. These divide into three major categories:
- Analytical
- Computational
- Experimental
For analytical methods, imagine someone at a chalkboard, white dust on their trousers, deriving lengthy, complicated hand equations. But hand equations still remain too simplistic to be accurate for anything but the most basic of scenarios.
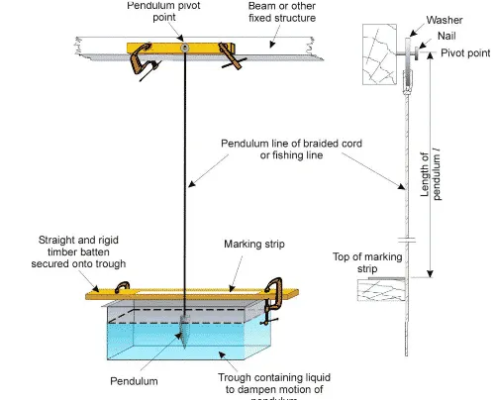
On the other end lies the experimental, requiring expensive testing facilities custom built for detailed experiments. (Figure 2‑1) These facilities are often targeted towards specific types of problems and experiments. So we can only test for known theories and designs. They restrict our ability to explore new possibilities.
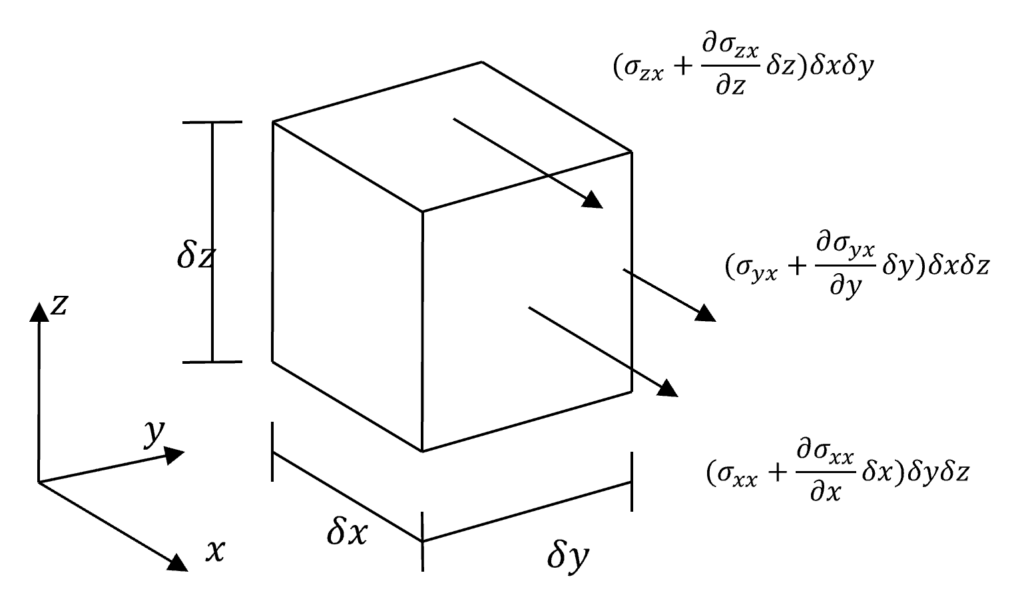
Computational methods offer a happy medium. They work like experimental methods, but we construct virtual test facilities on the computer. No construction costs, and infinite flexibility to customize the experiment for each purpose.